II. MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
A. Scrotum (cremaster)
Supports testes, cremaster muscle can move testes closer to or farther from body
B. Testes– Male gonad
1. Tunica albuginea
Dense white connective tissue covering testis
2. Lobules (200-300) – Compartments
3. Seminiferous tubules
Tightly coiled tubules where sperm are produced
Spermatogenesis (5-10 weeks) (300 million/day) – process of making sperm
1. Spermatogonia [mature, grow to become…]
2. Primary spermatocytes [meiosis I…]
3. Secondary spermatocytes [meiosis II…]
4. Spermatids
Haploid, matures to…
5. Spermatozoon
a. Head
-Nucleus
-Acrosome
b. Midpiece – numerous mitochondria
c. Tail – propels
4. Straight tubules
5. Rete testes – tubular network
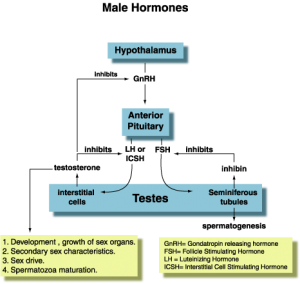
6. Interstitial cells (Leydig)
a. Testosterone
1. Sperm production
2. Sexual drive
3. Secondary sex characteristics
C. Puberty
1. Signs
2. Hormones
a. Testosterone made by interstitial cells of testes
b. GnRH = Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone, Stimulates pituitary gland to produce:
c. LH = ICSH – Interstitial cell stimulating hormone
d. FSH-Stimulates spermatogenesis
e. Inhibin
Inhibits FSH
D. Epididymis
Comma-shaped, posterior to testis
1. Head
Superior, receives sperm from testes
2. Body
3. Tail
Inferior, empties into ductus deferens
E. Ductus deferens (vas)
1. Spermatic cord
Includes ductus deferens plus vessels, nerves…
2. Inguinal canal
Passageway through body wall for spermatic cord
F. Urethra
1. Prostatic
2. Membranous
after prostate, before penis
3. Spongy = Penile
through penis to…
4. External urethral orifice
G. Accessory sex glands
1. Seminal vesicles
2. Prostate
3. Bulbourethral (Cowper’s)
4. Semen
Sperm plus liquids from accessory sex glands which nourishes sperm, buffers acid pH in vagina, helps to propel and activate sperm , 2 1/2 – 5 mls per ejaculate, about 300 million sperm
H. Penis
1. Erectile tissue
Vascular
2. Corpus cavernosum
Dorsolateral penis, responsible for most of erection
3. Corpus spongiosum
Erectile tissue surrounding urethra
4. Glans penis
Distal end of penis covered by…
5. Prepuce – Foreskin
I. Sexual responses
1. Erection
Penis enlargement and rigidity, vascular phenomenon, parasympathetic nerve impulses cause arteriole dilation
2. Emission
First part of male orgasm mediated by sympathetic nerve impulses resulting in propulsion of sperm to urethra and release of seminal fluids from accessory sex glands
3. Ejaculation
Contractions that result in release of semen from urethra