B. CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM – BLOOD VESSELS
1. Contrast arteries, veins, capillaries, arterioles, and venules.
2. Name the 3 layers in the wall of an artery or vein.
3. Describe the wall and function of a capillary.
4. Describe the differences in blood velocity in large vs small blood vessels.
5. Explain what causes a pulse.
6. Define blood flow, blood pressure, and resistance.
7. Name some factors that effect resistance.
8. Name the vessel that is most important in determining resistance to blood flow.
9. Describe the relationship of blood flow to pressure and resistance.
10. Describe the relationship of mean arterial pressure, cardiac output, and total peripheral resistance.
11. List the neural factors that influence arterial pressure and describe how they function.
12. Describe the effects of angiotensin, epinephrine, and ADH on arterial pressure.
13. Describe the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone interaction.
14. Describe how blood volume influences arterial pressure and describe the factors that influence blood volume.
15. Describe the measurement of blood pressure. What does systolic pressure correspond to? Diastolic pressure?
16. Define venous return and describe influencing factors.
17. Describe the movement of blood through veins.
18. Describe the effects of gravity on the cardiovascular system and what compensatory mechanisms exist to counteract these effects.
19. Describe the cardiovascular adjustments during exercise.
20 Trace the general path of blood through the heart chambers and valves, to the lungs, and back to the heart.
21. Explain the primary purpose of systemic circulation. Define systemic.
22. Systemic arteries arise from what main vessel?
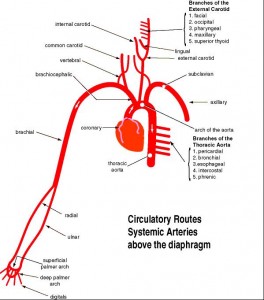
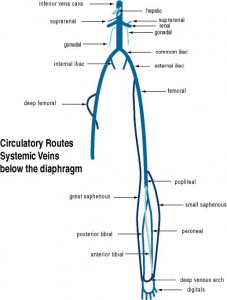
23. Trace the general path of blood from the heart through the systemic circuit and back to the heart. Know the general areas these vessels serve Include the following vessels:
ARTERIES:
1. Ascending aorta
2. Aortic arch
3. Brachiocephalic
4. Common carotid (R&L)
5. Subclavian (R&L)
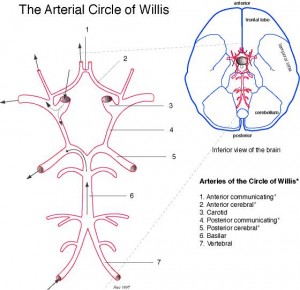
6. Vertebral (R&L)
7. Basilar
8. Circle of Willis
9. External carotid (R&L)
10. Internal carotid (R&L)
11. Lingual (R&L)
12. Axillary (R&L)
13. Brachial (R&L)
14. Ulnar (R&L)
15. Radial (R&L)
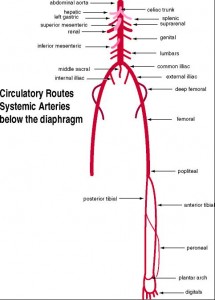
16. Descending aorta
17. Celiac
18. Hepatic
19. Left gastric
20. Splenic
21. Superior mesenteric
22. Suprarenal (R&L)
23. Renal (R&L)
24. Testicular (R&L)
25. Ovarian (R&L)
26. Inferior mesenteric
27. Lumbars
28. Common iliac (R&L)
29. Middle sacral
30. Internal iliac (R&L)
31. External iliac (R&L)
32. Femoral (R&L)
33. Popliteal (R&L)
34. Anterior & Posterior Tibial (R&L)
VEINS:
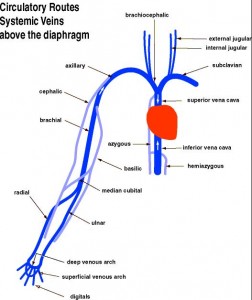
1. Superior vena cava
2. Inferior vena cava
3. Brachiocephalic (R&L)
4. Internal jugular (R&L)
5. External jugular (R&L)
6. Subclavian (R&L)
7. Axillary (R&L)
8. Cephalic (R&L)
9. Brachial (R&L)
10. Basilic (R&L)
11. Azygos
12. Hemiazygos
13. Common iliac (R&L)
14. Hepatic
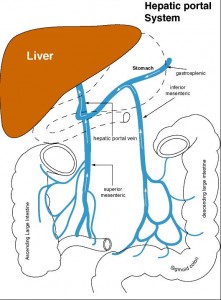
15. Hepatic portal
16. Superior mesenteric
17. Pancreatic
18. Gastric
19. Inferior mesenteric
20. Splenic
21. Suprarenal (R&L)
22. Renal (R&L)
23. Ovarian (R&L)
24. Testicular (R&L)
25. Internal iliac (R&L)
26. External iliac (R&L)
27. Femoral (R&L)
28. Popliteal (R&L)
29. Anterior & Posterior Tibial (R&L)
30. Great saphenous (R&L)
24. Describe the purpose of the hepatic portal circulation.
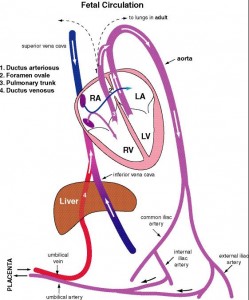
25. Name the fetal blood vessel that contains the highest concentration of oxygen.
26. Trace the path of blood in the fetus from the right atrium to the placenta and back to the right atrium. Explain how the fetal lungs and liver are bypassed.
Here are some comments on these blood vessel pathways: